Semiconductor Alloys: Physics and Materials Engineering for Microdevices - A Comprehensive Guide

5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 7063 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 364 pages |
Semiconductor alloys have revolutionized the world of microelectronics. These materials, composed of two or more semiconductor elements, exhibit unique properties that make them essential for a wide range of applications, from high-performance transistors to efficient light-emitting diodes (LEDs). This comprehensive article provides an in-depth exploration of semiconductor alloys, covering their physics, materials engineering, and applications in microdevices.
Semiconductor Alloys: Fundamentals
Semiconductor alloys are formed by combining two or more elements from the semiconductor group of the periodic table. When these elements mix, they create a new material with a unique bandgap, the energy difference between the valence and conduction bands. This bandgap determines the material's electrical and optical properties.
By carefully controlling the composition and proportions of the constituent elements, engineers can tailor the properties of semiconductor alloys to meet specific application requirements. This flexibility has made semiconductor alloys essential for advancing the capabilities of microdevices.
Materials Engineering of Semiconductor Alloys
The properties of semiconductor alloys are strongly influenced by their microstructure and composition. Materials engineers employ a range of techniques to synthesize and optimize these materials for specific applications.
- Crystal growth: Semiconductor alloys can be grown using various techniques, including molecular beam epitaxy, metalorganic chemical vapor deposition, and liquid phase epitaxy. These methods control the formation of the crystal lattice and ensure the desired composition and thickness of the alloy.
- Doping: Impurities are intentionally introduced into semiconductor alloys to modify their electrical properties. For example, adding a small amount of phosphorus or arsenic to silicon creates an n-type semiconductor, while adding boron creates a p-type semiconductor.
- Annealing: Heat treatment is used to improve the crystalline structure and reduce defects in semiconductor alloys. Annealing processes can also activate dopants and stabilize the material's properties.
Applications in Microdevices
Semiconductor alloys are the cornerstone of modern microdevices, powering everything from smartphones to supercomputers. Here are a few key applications:
- Transistors: Semiconductor alloys, such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) and indium phosphide (InP),enable the fabrication of transistors with higher electron mobility and faster switching speeds. These transistors are essential for high-performance electronic devices.
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs): Semiconductor alloys, such as gallium nitride (GaN) and indium gallium nitride (InGaN),are used to create efficient and bright LEDs. These LEDs are used in a wide range of applications, including displays, lighting, and sensors.
- Solar cells: Semiconductor alloys, such as cadmium telluride (CdTe) and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS),are used in thin-film solar cells. These solar cells are cost-effective and can be integrated into flexible or lightweight structures.
Emerging Technologies and Future Prospects
Research in the field of semiconductor alloys is continuously expanding, driven by the increasing demand for advanced microdevices. Here are a few emerging technologies that promise exciting future developments:
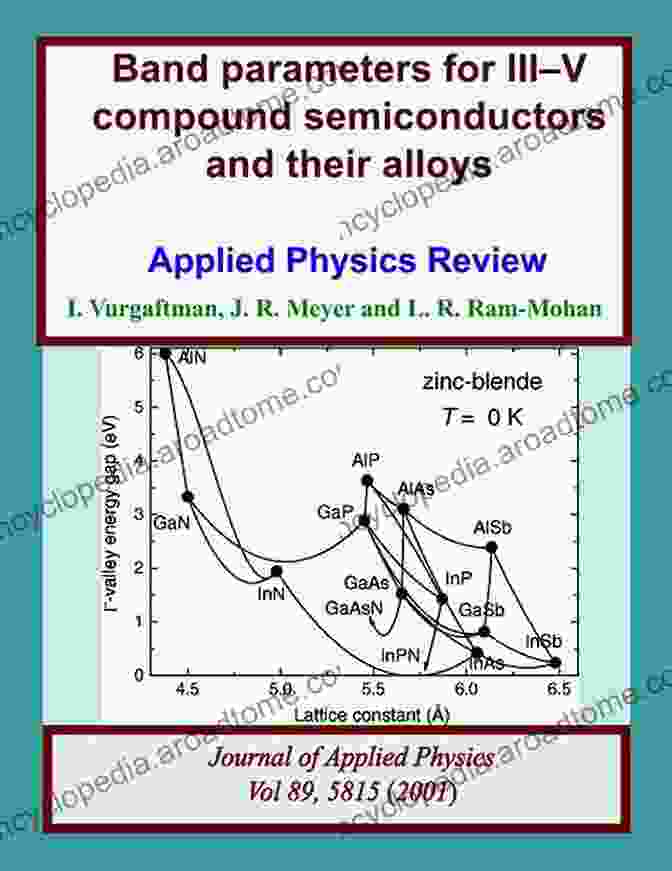
- III-V compound semiconductors: III-V compound semiconductors, such as gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) and indium gallium arsenide nitride (InGaAsN),offer unique optoelectronic properties. These materials have applications in high-speed lasers, infrared detectors, and solar cells.
- Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors: 2D semiconductors, such as graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides, exhibit exceptional electrical and optical properties. These materials have the potential to revolutionize the design and performance of microdevices.
- Metamaterials: Metamaterials are artificial materials designed to exhibit electromagnetic properties not found in nature. Semiconductor alloys can be used as building blocks for metamaterials, enabling the development of novel optical devices and sensors.
Semiconductor alloys are the fundamental building blocks of modern microdevices, enabling the development of cutting-edge technologies that shape our lives. This article provided a comprehensive overview of the physics, materials engineering, and applications of semiconductor alloys. As research continues to push the boundaries of these materials, we can anticipate even more transformative advancements in the future of microelectronics and beyond.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 7063 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 364 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Os Hillman
Os Hillman Gerhard Zarbock
Gerhard Zarbock Robert S Gotlin
Robert S Gotlin Fun Facts Freddie
Fun Facts Freddie John Fiske
John Fiske Liane Schneider
Liane Schneider John F Dooley
John F Dooley John Tillman Lyle
John Tillman Lyle 1st Ed 2019 Edition Kindle Edition
1st Ed 2019 Edition Kindle Edition Ian Brady
Ian Brady Paul O Brien
Paul O Brien 1989th Edition Kindle Edition
1989th Edition Kindle Edition Bill Wilson
Bill Wilson 12th Edition Kindle Edition
12th Edition Kindle Edition Jill Wellington
Jill Wellington Alinka Rutkowska
Alinka Rutkowska Louis D Hayes
Louis D Hayes Cris Danneville
Cris Danneville U M Fatima
U M Fatima Il Sung Na
Il Sung Na
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!
 Dave SimmonsBone SPECT CT of Ankle and Foot: The Ultimate Diagnostic Tool for Accurate...
Dave SimmonsBone SPECT CT of Ankle and Foot: The Ultimate Diagnostic Tool for Accurate... Dean CoxFollow ·16.4k
Dean CoxFollow ·16.4k Edward ReedFollow ·13.8k
Edward ReedFollow ·13.8k Ernest HemingwayFollow ·17.7k
Ernest HemingwayFollow ·17.7k Orson Scott CardFollow ·12.7k
Orson Scott CardFollow ·12.7k Federico García LorcaFollow ·10.2k
Federico García LorcaFollow ·10.2k Bradley DixonFollow ·18.5k
Bradley DixonFollow ·18.5k Joel MitchellFollow ·5.8k
Joel MitchellFollow ·5.8k José SaramagoFollow ·19.5k
José SaramagoFollow ·19.5k

 Desmond Foster
Desmond FosterBreak Free from the Obesity Pattern: A Revolutionary...
Obesity is a global pandemic affecting...

 Jared Nelson
Jared NelsonRobot World Cup XXIII: The Ultimate Guide to Advanced...
The Robot World Cup XXIII: Lecture Notes in...

 Charlie Scott
Charlie ScottFirst International Conference TMM CH 2024 Athens...
Prepare for...

 Finn Cox
Finn CoxRe-Capturing the Conversation about Hearing Loss and...
Challenging...

 Camden Mitchell
Camden MitchellJourney into the Realm of Digital Systems: An Immersive...
In the ever-evolving technological...

 Javier Bell
Javier BellUnveiling the Toxins Behind Multiple Sclerosis: A...
Multiple sclerosis...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 7063 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 364 pages |