Si Detectors and Characterization for HEP and Photon Science Experiments: Unlocking the Secrets of the Universe

The quest for unlocking the mysteries of the cosmos has led to the development of sophisticated scientific instruments. Silicon (Si) detectors play a pivotal role in these instruments, serving as sensitive sensors that collect and measure particles emanating from high-energy physics (HEP) experiments and photon science applications. This article delves into the intricate details of Si detectors and their characterization techniques, exploring their fundamental principles and applications in cutting-edge scientific research.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 37287 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 273 pages |
Principles of Si Detectors
Si detectors are solid-state devices that exploit the electrical properties of silicon to detect charged particles. When a charged particle traverses the silicon, it ionizes the atoms, creating electron-hole pairs. These charge carriers are then separated by an electric field applied across the detector, generating an electrical signal that is proportional to the energy deposited by the particle.
The detection efficiency and energy resolution of Si detectors are crucial parameters. Detection efficiency refers to the probability of detecting a particle that enters the detector, while energy resolution measures the detector's ability to distinguish between particles of different energies. The thickness and doping profile of the silicon affect these parameters.
Types of Si Detectors
Various types of Si detectors have been developed to meet the specific requirements of different HEP and photon science experiments. Some commonly used types include:
- Strip detectors: These detectors are characterized by narrow strips of silicon electrodes that collect charge carriers. They provide precise spatial resolution in one dimension.
- Pixel detectors: Pixel detectors are two-dimensional arrays of small silicon cells, each acting as an independent detector. They offer high spatial resolution in both dimensions.
- Microstrip detectors: Microstrip detectors combine features of strip and pixel detectors. They have narrow strips of electrodes but also include an additional layer of silicon to enhance charge collection.
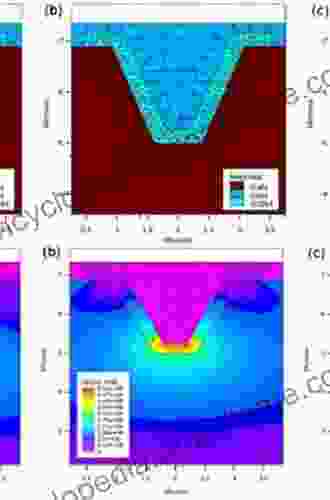
- 3D detectors: 3D detectors have electrodes embedded within the silicon bulk, allowing for improved detection efficiency, particularly for high-energy particles.
Characterization Techniques
Thorough characterization is essential to evaluate the performance of Si detectors and ensure their reliability in scientific experiments. Several techniques are employed for this purpose:
- Current-voltage measurements: These measurements determine the electrical properties of the detector, including leakage current and depletion voltage.
- Capacitance-voltage measurements: This technique evaluates the capacitance of the detector as a function of applied voltage, providing insights into the charge carrier concentration and depletion region.
- Particle beam testing: Particle beams are used to measure the detection efficiency, energy resolution, and spatial resolution of the detector.
- Noise measurements: Noise characterization assesses the amount of electronic noise present in the detector, which can affect its sensitivity.
Applications in HEP and Photon Science
Si detectors are indispensable components in a wide range of HEP and photon science experiments. Some notable applications include:
- Particle tracking: Si detectors are used to track the trajectory of charged particles in experiments such as the Large Hadron Collider (LHC).
- Vertex reconstruction: Si detectors provide precise spatial resolution for reconstructing the vertices of particle interactions, which helps identify the primary interaction point.
- Radiation monitoring: Si detectors are used to monitor radiation levels in particle accelerators and other experimental environments.
- X-ray and gamma-ray detection: Si detectors are employed in photon science experiments for detecting X-rays and gamma rays from various sources.
Si detectors are essential tools in the pursuit of scientific discovery. Understanding their principles, types, and characterization techniques is crucial for optimizing their performance and ensuring the success of HEP and photon science experiments. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of Si detectors, highlighting their fundamental concepts and applications. As research continues to push the boundaries of scientific exploration, Si detectors will undoubtedly play an increasingly significant role in unlocking the mysteries of the universe.
Relevant Long Descriptive Keywords for Alt Attribute:
* Detailed schematic diagram of a silicon detector * Microscopic image of a pixel detector * Graph illustrating the detection efficiency of a microstrip detector * Experimental setup for particle beam testing of a 3D detector * Application of Si detectors in the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 37287 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 273 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Saludable Mente
Saludable Mente Robert Greene
Robert Greene Julie Byrne
Julie Byrne Carlos Grider
Carlos Grider B Marsh
B Marsh Edward F Gilman
Edward F Gilman Dr Peter S Ruckman
Dr Peter S Ruckman Carrie Bohlig
Carrie Bohlig Karen Gadd
Karen Gadd Kelly Davio
Kelly Davio Wesley Gibbs
Wesley Gibbs Herman Melville
Herman Melville Marvin Lin
Marvin Lin Jennifer M Potter
Jennifer M Potter 13th Edition Kindle Edition
13th Edition Kindle Edition Tom Adams
Tom Adams Todd Glass
Todd Glass Ping Lu
Ping Lu Barbara Marx Hubbard
Barbara Marx Hubbard Charlotte Rivers
Charlotte Rivers
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Mario Vargas LlosaInnovation Incubation and Entrepreneurship: Revolutionize How You Innovate...
Mario Vargas LlosaInnovation Incubation and Entrepreneurship: Revolutionize How You Innovate... Geoffrey BlairFollow ·12.4k
Geoffrey BlairFollow ·12.4k Elias MitchellFollow ·9.8k
Elias MitchellFollow ·9.8k Kenneth ParkerFollow ·16.5k
Kenneth ParkerFollow ·16.5k Kelly BlairFollow ·19.1k
Kelly BlairFollow ·19.1k Vladimir NabokovFollow ·17.3k
Vladimir NabokovFollow ·17.3k Julio Ramón RibeyroFollow ·10.1k
Julio Ramón RibeyroFollow ·10.1k Sammy PowellFollow ·14.9k
Sammy PowellFollow ·14.9k Federico García LorcaFollow ·10.2k
Federico García LorcaFollow ·10.2k

 Desmond Foster
Desmond FosterBreak Free from the Obesity Pattern: A Revolutionary...
Obesity is a global pandemic affecting...

 Jared Nelson
Jared NelsonRobot World Cup XXIII: The Ultimate Guide to Advanced...
The Robot World Cup XXIII: Lecture Notes in...

 Charlie Scott
Charlie ScottFirst International Conference TMM CH 2024 Athens...
Prepare for...

 Finn Cox
Finn CoxRe-Capturing the Conversation about Hearing Loss and...
Challenging...

 Camden Mitchell
Camden MitchellJourney into the Realm of Digital Systems: An Immersive...
In the ever-evolving technological...

 Javier Bell
Javier BellUnveiling the Toxins Behind Multiple Sclerosis: A...
Multiple sclerosis...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 37287 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 273 pages |